How You Hear Northland Audiology
Inner ear: The inner ear, also called the labyrinth, operates the body's sense of balance and contains the hearing organ. A bony casing houses a complex system of membranous cells. The inner ear.

Human ear anatomy. Ears inner structure, organ of hearing ve (1000410
In these topics. Dizziness and Vertigo Introduction to Inner Ear Disorders. Global Medical Knowledge. The BioDigital Human is a virtual 3D body that visualizes human anatomy, disease and treatments in an interactive 3D web platform.
Ear Anatomy Causes of Hearing Loss Hearing Aids Audiology
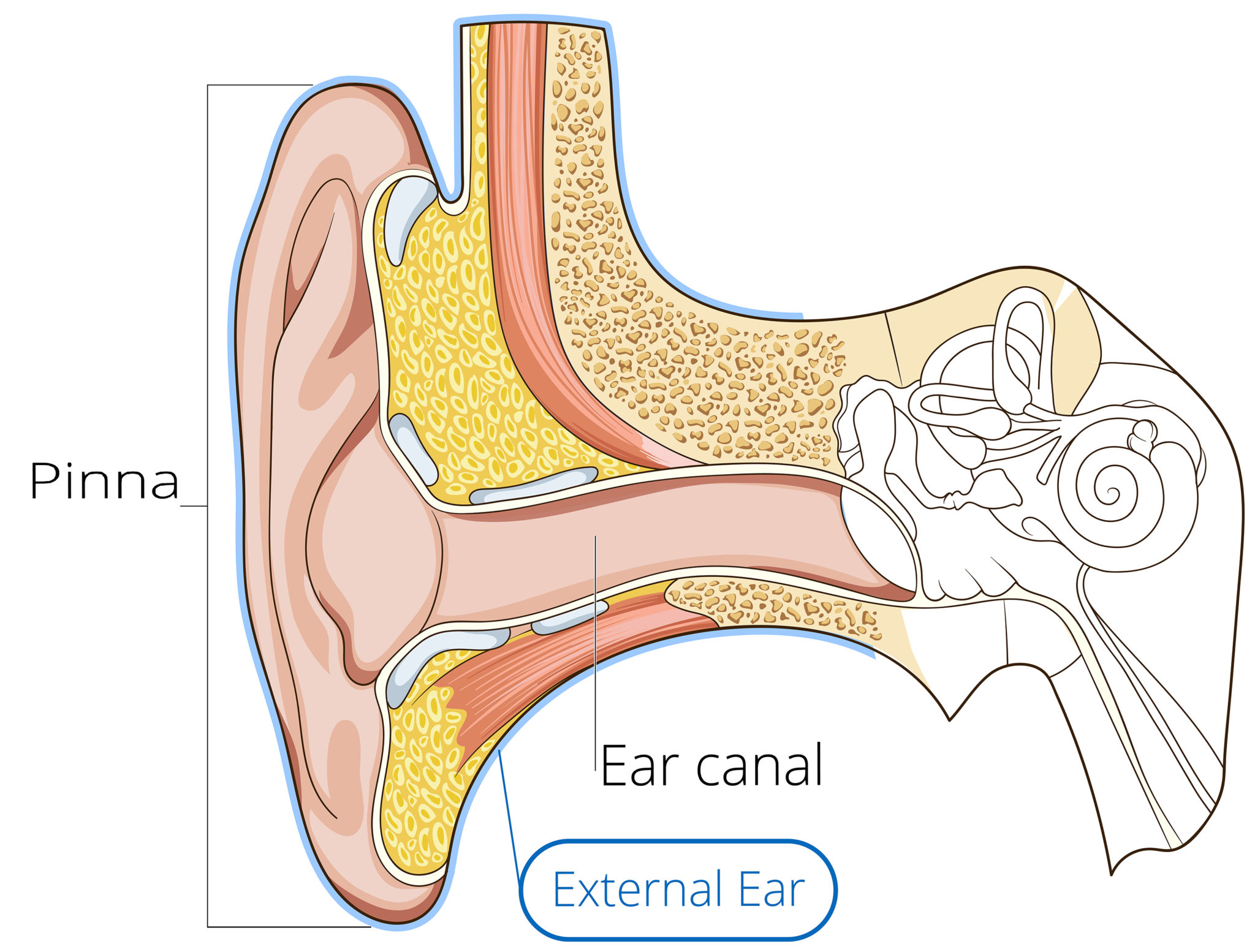
Internal ear This mixture of bones, nerves, vessels, membranes, and muscles that make up the ear will be described in this article. Contents External ear Auricle External acoustic meatus Tympanic membrane Muscles of the external ear Vasculature of the external ear Innervation of the external ear Middle ear Tympanic cavity Auditory ossicles

Inner Ear Problems Causes & Treatment of inner ear Dizziness & Vertigo
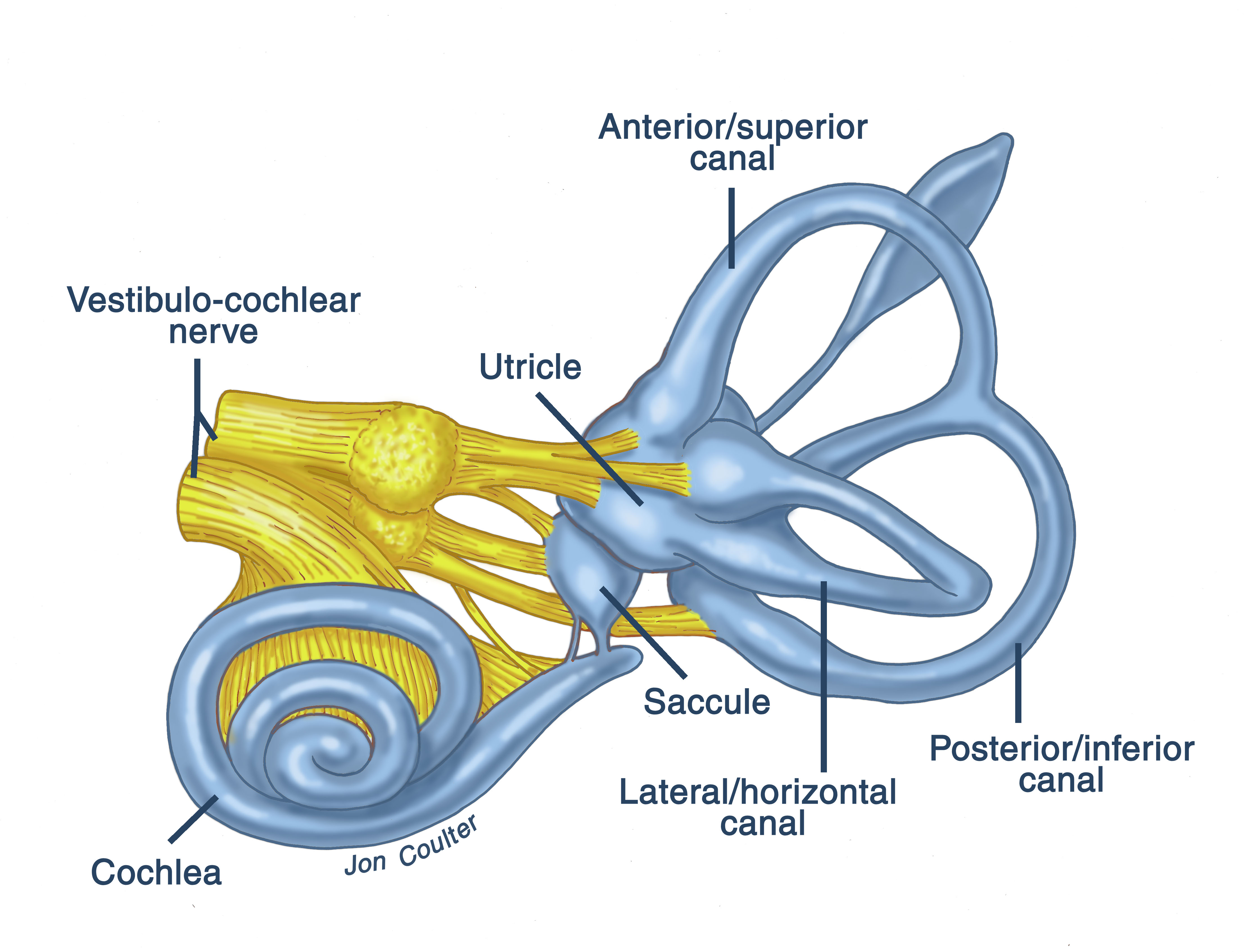
inner ear, part of the ear that contains organs of the senses of hearing and equilibrium.The bony labyrinth, a cavity in the temporal bone, is divided into three sections: the vestibule, the semicircular canals, and the cochlea.Within the bony labyrinth is a membranous labyrinth, which is also divided into three parts: the semicircular ducts; two saclike structures, the saccule and utricle.
Ear infections explained Dr Mark McGrath
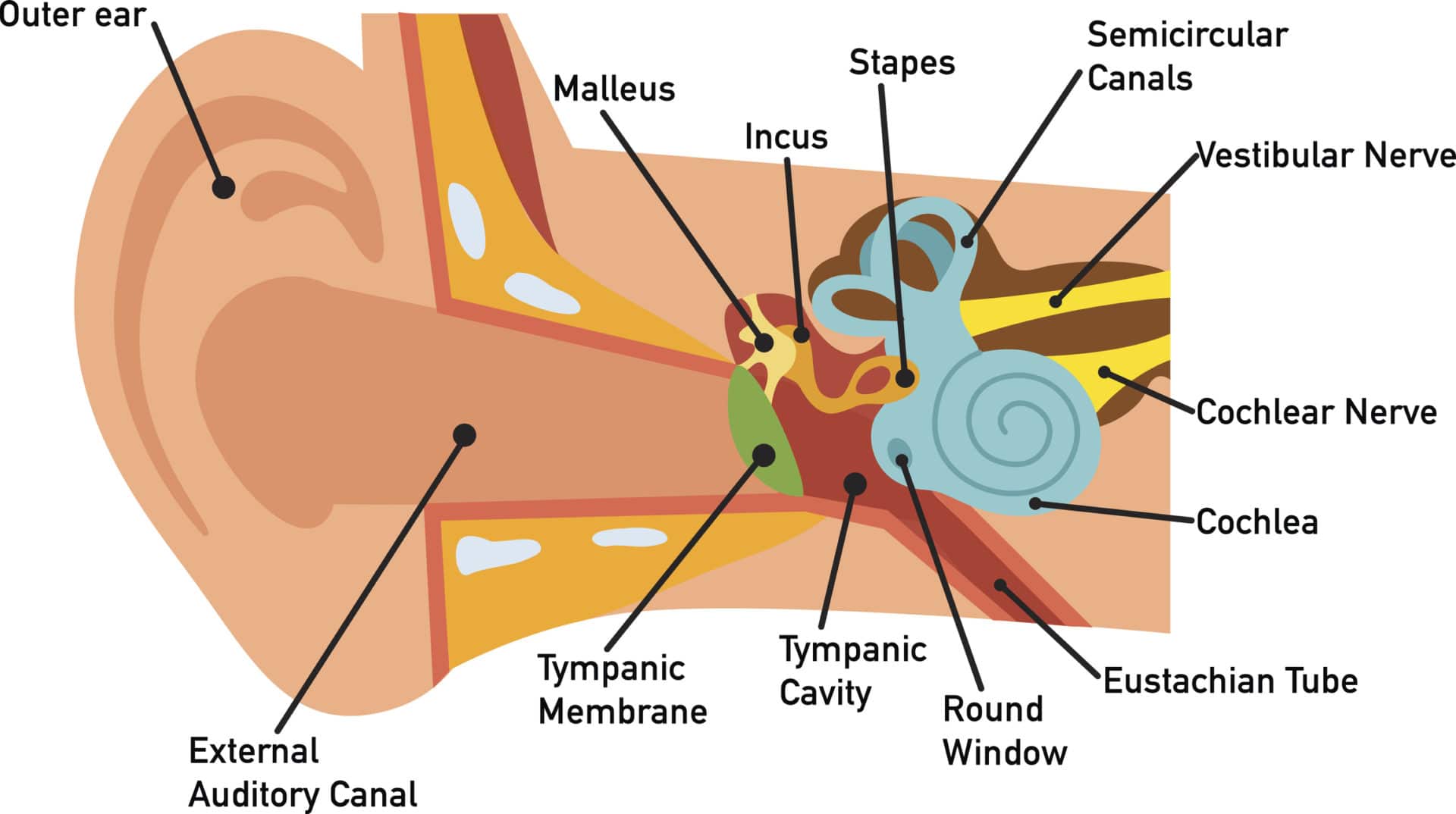
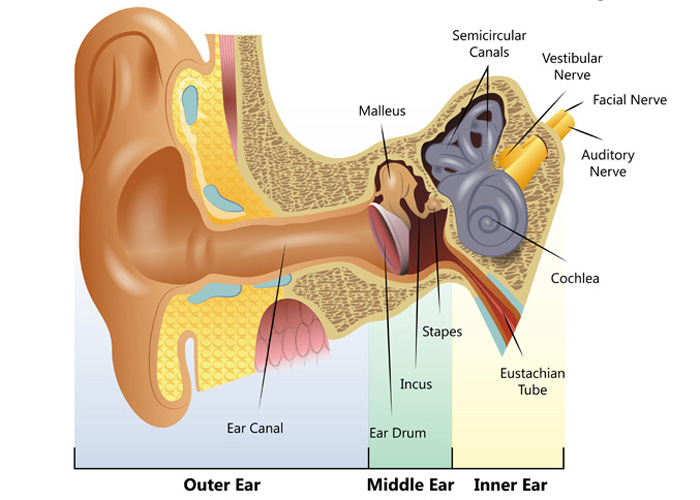
In this diagram we visualise the inner ear. The cochlea is supplied by the cochlear nerve. The utricle, some of the saccule, the lateral semicircular canal and the superior semicircular canal are all supplied by the superior vestibular nerve. The posterior canal is supplied via the inferior vestibular nerve.
What is a balance disorder? Hearing Link
Inner Ear Anatomy. The inner ear is where the sound waves are translated into types of electrical nerve impulses. Most of the hearing and balance content is located within the bony labyrinth. After the tympanic membrane, these are the nerves that most likely contribute to hearing impairment and may require treatment or medical services [1].

Outer Ear Anatomy Outer Ear Infection & Pain Causes & Treatment
The inner ear consists of the bony labyrinth and membranous labyrinth. The bony labyrinth comprises three components: Cochlea: The cochlea is made of a hollow bone shaped like a snail and divided into two chambers by a membrane.

Alila Medical Media Human ear anatomy, labeled diagram. Medical
Ear Anatomy Schematics. Ear Anatomy Images. Chapter 4 - Fluid in the ear. Fluid in the ear Discussion. Fluid in the ear Outline. Middle Ear Ventilation Tubes. Fluid in the ear Images. Chapter 5 - Traveler's Ear. Traveler's Ear Discussion.
How does your ear work?
Anatomy What are the parts of the inner ear? Your inner ear has three main parts: your cochlea, semi-circular canals (labyrinth) and your vestibule. Your cochlea supports your hearing and your vestibule and semi-circular canals support your balance. What is the cochlea?

Vertigo Have You Spinning Chiropractic Home Care Ear anatomy, Human
Inner ear anatomy. The outer, middle, and inner ear. The inner ear is at the end of the ear tubes. It sits in a small hole-like cavity in the skull bones on both sides of the head. The inner ear.

Hearing Loss Regenerated in Damaged Mammal Ear The Personal Longevity
Your outer ear and middle ear are separated by your eardrum, and your inner ear houses the cochlea, vestibular nerve and semicircular canals (fluid-filled spaces involved in balance and hearing). What is the ear? Your ears are organs that detect and analyze sound. Located on each side of your head, they help with hearing and balance. Advertisement

Ear Anatomy Vestibular Disorders Association
Labelled Diagram of Inner Ear Inner Ear - Description The inner ear or labyrinth of the human ear comprises 2 structures - the bony labyrinth and the membranous labyrinth. Bony labyrinth is a series of cavities or channels present in the petrous part of the temporal bone. The membranous labyrinth is present within the bony labyrinth.

Inner Ear Discovery Helps Explain How Sound Waves Brain Signals
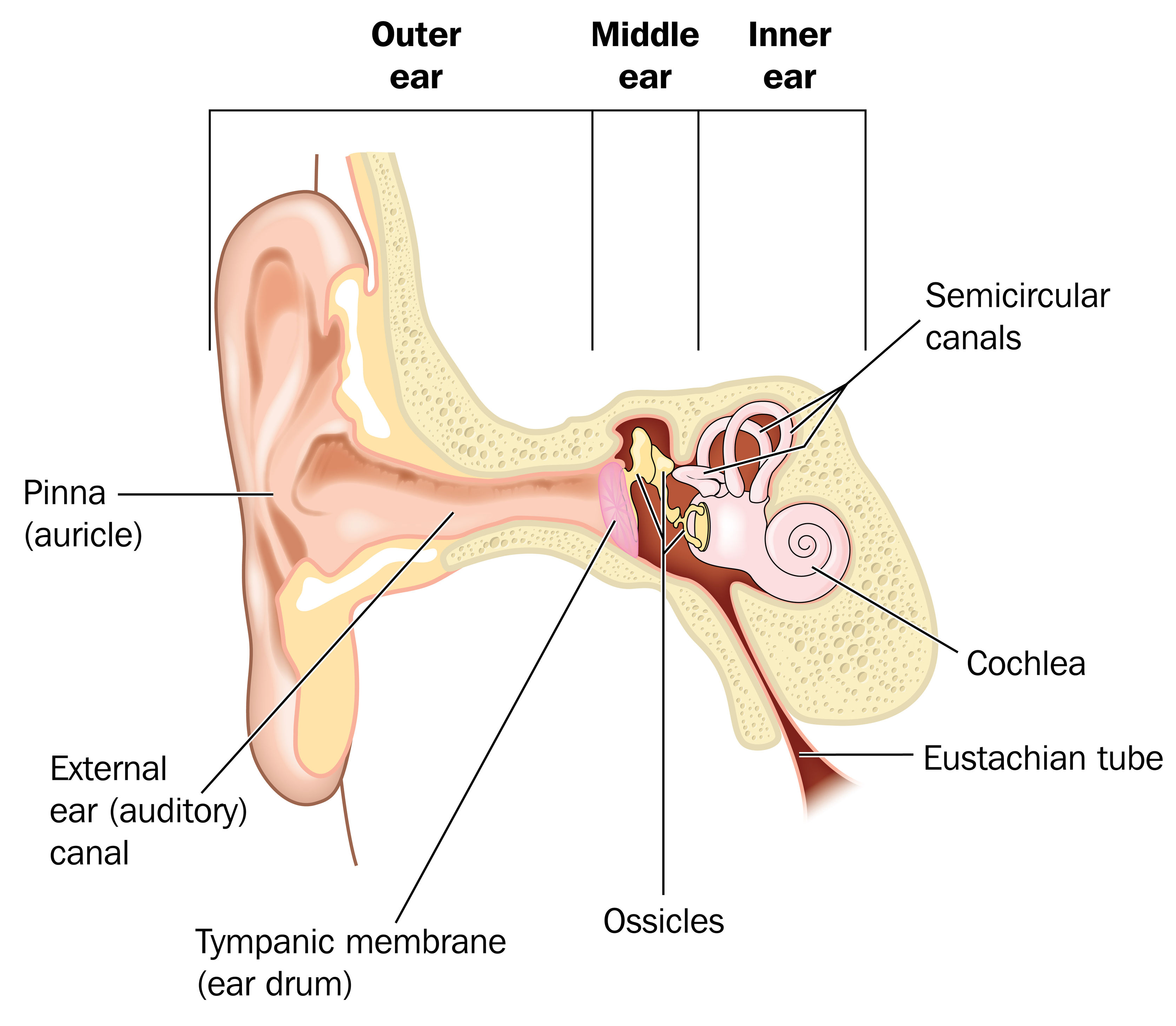
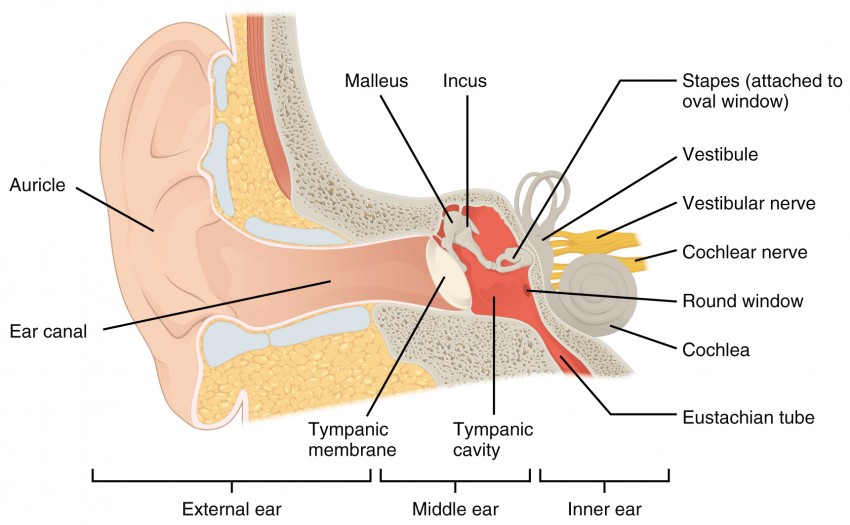
The middle ear includes the eardrum, malleus, incus, and stapes. The inner ear includes semicircular canals, eustachian tube, cochlea, and vestibule and auditory nerves.">.
Audition and Somatosensation Anatomy and Physiology I
The outer ear consists of the visible portion called the auricle, or pinna, which projects from the side of the head, and the short external auditory canal, the inner end of which is closed by the tympanic membrane, commonly called the eardrum. The function of the outer ear is to collect sound waves and guide them to the tympanic membrane.

Human Ear Anatomy Parts of Ear Structure, Diagram and Ear Problems
The inner ear is embedded within the petrous part of the temporal bone, anterolateral to the posterior cranial fossa, with the medial wall of the middle ear, the promontory, serving as its lateral wall.

Labeled Diagram Of the Ear Inspirational Losing sound Ear anatomy
The ear is structurally divided into three parts: the outer (external), middle and inner ear. The middle ear is an air-filled pressurized space within the petrous portion of the temporal bone, extending from the tympanic membrane (eardrum) to the lateral wall of the inner ear. It is lined by mucous membrane and communicates with the nasopharynx.